The Landing of The Schwenkfelders from St Andrew 1734, Oil Painting by Adolf Pannash
The Schwenkfelders, a group of people who followed the teachings of Caspar Schwenkfeld, came to America from Silesia (at the time Silesia was part of Germany, currently it is part of Poland) to flee religious persecution. Because they were unwilling to conform to the Catholic, or Lutheran, teachings, they were persecuted in Silesia. From 1580-1799 they were put in prisons, taken to Vienna forced to work in the trenches and chained to the galleys to serve in the war against the Turks. In later years, they were forced to bury their dead in the driftways where the cattle were gathered, with no ceremony, and no relatives or friends permitted to attend the burial. One prisoner wrote ""One would crawl away from such a Christianity if one could not run."
There was a brief reprieve in their persecution during the 30 year war, 1618-48, while attentions were diverted to the war. But the reprieve did not last.
In 1725 an edict was granted that all of the Schwenkenfeld children must be catechized, or they would be removed from their families and placed in Catholic homes. Faced with losing their children, the Schwenkfelders began to plan their escape.
First they traveled to Saxony, and for 7 years they enjoyed peace under the protection of Count Zinzendorf. The Count wanted to form one unified church with the Moravians and Schwenkfelders, among others, but the groups preferred to meet on their own in private homes. On July 17 1732 the Austrian Empire requested information on the Schwenkfelds from the Count, and he was ordered to remove no one else from their empire. On April 4, 1733, the Count was advised by an official of the Saxon government that the Schwenkfelders could no longer be protected. They Saxon government gave them one year to prepare for departure.
"Meanwhile, in 1730 and 1731, three sons of one of several Schultz families had ventured forth from Saxony to Holland to engage in the saffron trade. One went to the Dutch East Indies, one remained in Holland, and the third went to Pennsylvania. In 1733 the remaining members of the family also migrated to Pennsylvania. Accounts of their safe arrival and entire satisfaction came back to the group in Saxony. Pennsylvania now seemed to be their definite goal. Count Zinzendorf and the Moravians became interested in a colony in Georgia, and the Schwenkfelders were willing to consider Georgia as a possibility, but their conditions were not met and the project fell through.
Having secured permission from the English government to settle in Pennsylvania, the Schwenkfelders started on their journey. . On April 20, 1734, the first family left Saxony on thetrek to the Elbe River, fifty or more miles westward. They had been advised not to travel in one body for fear of attracting attention. Emigration was looked upon with disfavor. Moreover, their former persecutors in Silesia might intercept them. Other family groups followed daily, at intervals, for eight days until forty families numbering 180 individuals had arrived at Pirna on the Elbe, above Dresden. When all had assembled there, they embarked on the same day on boats for Hamburg-Altona where Mennonite merchants, the Van der Smissen family, to whom the Schwenkfelders had been commended by their erstwhile Holland benefactors, provided food and lodging gratis for eleven days, engaged three sailing vessels, and paid for their passage to Holland.
On the North Sea a violent storm separated the vessels. Each feared the others lost, but all arrived safely. In Haarlem another merchant family, van Buissant, entertained them for fifteen days, engaged an English sailing vessel (the St. Andrew, John Stedman, Captain) to convey them across the Atlantic. They also lavished upon them provisions for the voyage, gave them money for the poor when they reached Pennsylvania, and paid the passage thither for the whole group, in spite of the Schwenkfelders' grateful protest.
On June 28, 1734, they sailed from Rotterdam. Palatines swelled the number of passengers on board to three hundred. A diary of the entire journey, written by Christopher Schultz, an orphan sixteen years of age, relates that at one point the vessel lay still for a long while in a great calm. At another time a violent storm dashed the waves over the side of the ship, drenching their bedding and baggage. Their books, still preserved, show the water stains. Death took nine of their number: six little children, a young man of twenty years, a young mother, and an aged grandmother.
The bodies were weighted and committed to the sea.
The St. Andrew docked at Philadelphia, September 22 (New Style), 1734. The captain's list of passengers is preserved in the Schwenkfelder Library, Pennsburg, Pennsylvania. On the 23rd all males sixteen years of age and over were required to promise allegiance to the King of Great Britain and to the Proprietor of the Province. This document with signatures appended is also preserved.
On the following day, September 24, George Weiss, their spiritual leader, conducted an all-day Thanksgiving Service., This day of Remembrance and Thanksgiving has been observed by the Schwenkfelders in Pennsylvania annually to the present time, at first in their log-cabin homes and barns, or under the open sky, if weather permitted; later in their school and meeting houses; and latterly in their modern church edifices. This day has never been vulgarized by feasting. It is observed as a day of worship, thanksgiving, remembrance, spiritual edification, and new vision. The vast and intriguing panorama of the New World now lay stretched out before them. Like panting deer who have escaped the hunter's missiles, the little company separated and scattered into Penn's Woods. Unable to acquire a large tract of land whereon all of them could settle in close proximity to each other, the individual families settled in different localities, wherever smaller tracts were available, within a radius of about fifty miles northwestward of Philadelphia in what are now the counties of Montgomery, Bucks, Berks, and Lehigh; at Germantown, ChestnutHill, Towamencin, Skippack, Frederick, Goshenhoppen, Milford, Macungie, and Oley. In 1767, David Schultz, a surveyor, drafted two maps showing the location of the different families. These he sent to the friends and relatives who had remained in Silesia. The same maps were found in the parish house in old Harpersdorf and brought back in 1919 to the Schwenkfelder Library in Pennsburg,
built on land originally owned by the surveyor." - from the Schwenkfelders in PA by Schultz
Resources:
The Schwenkfelders In Pennsylvania by Selena Schultz
http://heathersgen.blogspot.com/2013/12/the-schwenkfelders-of-pennsylvania-by.html
The Schwenkfelders, A Historical Sketch by Hedrick
http://heathersgen.blogspot.com/2013/12/the-schwenkfelders-historical-sketch-by.html
Schwenkfelder Marriages (Including Cake Recipe)
http://heathersgen.blogspot.com/2013/12/schwenkfelder-marriages.html
The Schwenkdenfelders & Apple Butter
http://heathersgen.blogspot.com/2013/12/the-schwenkfelder-immigration.html
Schwenkenfelder Hymnology
https://archive.org/details/schwenkfelderhy00seipgoog
The Schwenkfelder Library & History Center
http://www.schwenkfelder.com/
The Schwenkfelder Exile Society
http://schwenkfelderexilesociety.org/
Our Connections:
(Through Dan's Paternal Lines)
Dan, pointing to one of his ancestors on the Immigration List painting at the Schwenkfelder Library
The Brown/Truckenmiller Connection to the Schwenkfelders:Beyer Line to Thelma Clara (Brown) Truckenmiller
Yeakel Line to Thelma Clara (Brown) Truckenmiller
Kreibel Line to Thelma Clara (Brown) Truckenmiller
Anders Line to Thelma Clara Brown
Melchoir Beyer married Eva Unknown
Abraham BEER (BEYER) 1690 - 1754 married Rosina JAECKEL (YEAKEL) 1699-1770
Anna Maria Beyer 1720-1802 married Abraham Jackel Yeakel 1720-1768
David Yeakel 1762-1820 married Anna Kreibel 1766-1841Maria Yeakel 1791-1854 married Daniel HeinDavid Hein married Sarah MauserThelma Brown married Ward Welsh TruckenmillerCharles "Fred" Truckenmiller married Patsy Ann SmithDaniel Truckenmiller married Heather Sulouff ---------------------------------------------
furniture on display in the Schwenkfelder Musuem
" The Schwenkfelders endured years of oppression. Enslaved on ships, jailed, fined and put in stocks, they were not allowed freedom of worship sporadically for 150 years. Persecution sometimes came from Lutherans or Catholics, and often from government officials. The Schwenkfelders were subject to changes in the political climate, which were frequent and severe.By 1700, all Schwenkfelders were living the village of Harpersdorf and the surrounding area. Two Jesuit priests were sent to the region in 1719 to convert them to Roman Catholicism by order of the Emperor. At first, the priests imposed a few rules, but they soon found that the Schwenkfelder spirit was not easy to break and persecution intensified. Prohibition of Schwenkfelder burials on consecrated ground was among the sanctions exacted by the Jesuits. The Schwenkfelders instead were forced to bury their dead in potters' fields outside Harpersdorf. The Jesuits did not allow any of the Schwenkfelders to sell their property and leave town.
In the early 1720s appeals were made in Vienna for toleration,but were rejected. By 1726, many of the families were desperate to escape. Their leaders secretly contacted Count Nicholas Ludwig von Zinzendorf in Berthelsdorf, Saxony, for shelter. Four years before, Zinzendorf had provided a home to the Moravians, another Protestant sect. Beginning in February 1726 and continuing into the following months, families quietly crept from their homes in Harpersdorf at night. Over 500 of the faithful would take this fateful path. They fled with only the clothes on their backs and a few hand carried items, across the border to Saxony and their unknown future.
They decided to settle in Pennsylvania, already home to German immigrants and others seeking religious freedom. They arrived at the port of Philadelphia in six migrations from 1731 to 1737. The largest group of Schwenkfelders set sail on the St. Andrew from Haarlem, Holland in June, 1734. After a grueling and often tragic voyage, they landed at Philadelphia on September 22, 1734. On the following day, the Schwenkfelder men over age 16 took an oath of allegiance to the British crown, either by signing the oath or by a handshake. George Weiss, a self-educated Schwenkfelder pastor, held the first Day of Remembrance, or Gedächtnestag, on September 24. Each year on the Sunday closest to September 24, Schwenkfelders gather to honor their past. While sharing the simple meal of bread and butter, apple butter and water, today's Schwenkfelders remember what the immigrants endured for their faith. Gedächtnestag is the oldest continually celebrated day of thanksgiving in the United States."
http://schw enkfelder.com/museum/SchwenkfelderGallery.htm
Schwenkfelder immigration
The Schwenkfelders were a small, pietistic sect that emigrated from southern Germany and lower Silesia in the Austrian Empire beginning in 1731. After being persecuted for two centuries, and denied the right to Christian burial, they decided to follow like-minded German immigrants to the Pennsylvania colony where religious freedom was guaranteed. They arrived in Philadelphia in six migrations between 1731 to 1737, with the largest group of 200 sailing from Rotterdam in 1734. They settled farmsteads around Philadelphia, especially in modern Berks and Lehigh Counties. By 2003, almost all Schwenkfelders had joined more established Christian denominations, though many still claimed to be followers of the old doctrine. Schwenkfelders followed the teachings of Caspar Schwenckfeld von Ossig (1489–1561), a devout Catholic and member of the Silesian nobility. He was drawn to Martin Luther’s reform teachings but disagreed with him over the exact nature of the Lord’s Supper and the baptism of infants. Schwenckfeld believed that the Bible should not be literally interpreted or used as a “paper pope” but rather that believers should trust the Holy Spirit for insight into its meaning. Family was central to Schwenkfelder worship, with house churches the norm. As a result, the Society of Schwenkfelders was loosely organized, and its members freely associated with more established churches, where they could share their gifts of spiritual insight. In 2003, there was still an organized church, consisting of five congregations and about 2,600 members associated with the United Church of Christ, though many who claim Schwenkfelder roots are associated with the religious work of the Evangelical Lutherans, Presbyterians, American Baptists, the Christian Missionary Alliance, the Evangelical Association, and the Holiness Movement.
http://immigration-online.org/265-schwenkfelder-immigration.html
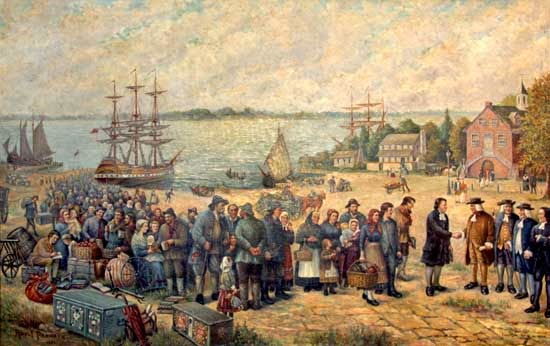

.jpg)




No comments:
Post a Comment